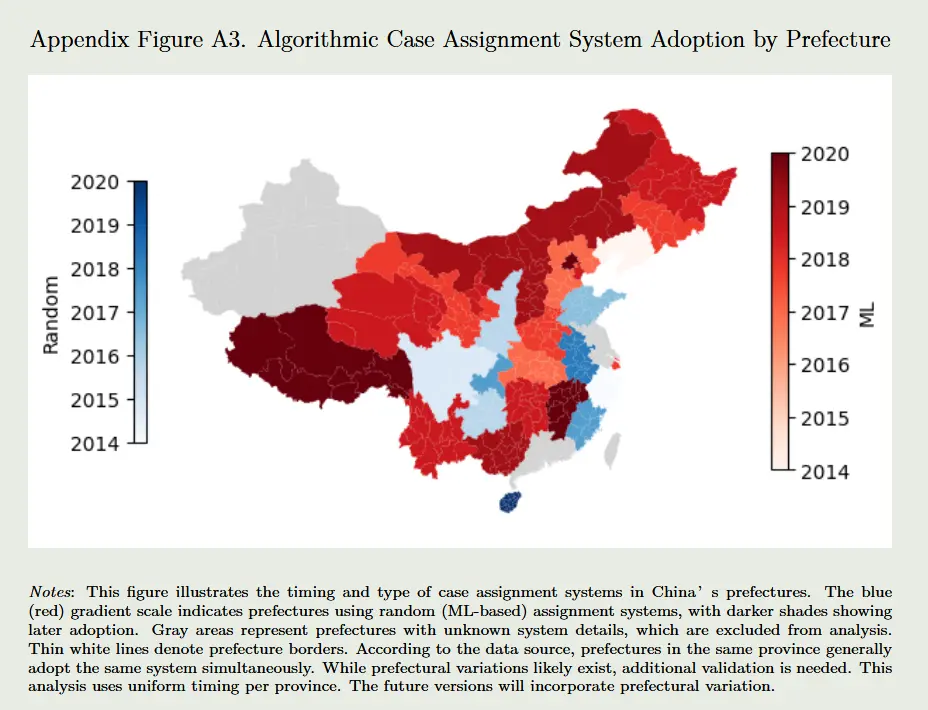
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
|
!pip install opencv-python
import cv2
import numpy as np
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
# 全局变量
random_colors = None
random_interp = None
ml_colors = None
ml_interp = None
img_rgb = None # 原始图片的 RGB 格式
img_raw = None # 原始图片的 BGR 格式 (用于显示和临时绘图)
img_with_rois = None # 带有永久绘制的 ROI 框的图片
# 全局变量用于 ROI 选择
roi_points = [] # 存储点击的 (x, y) 坐标
# ROI 选择阶段的状态机:
# 0: 准备选择 '随机分案' 色标的起点 (等待第一次点击)
# 1: 选择 '随机分案' 色标的终点 (第一次点击已发生,等待第二次点击)
# 2: '随机分案' 色标已选定,准备选择 '机器学习' 色标的起点 (等待第三次点击)
# 3: 选择 '机器学习' 色标的终点 (第三次点击已发生,等待第四次点击)
# 4: 两个色标均已选定,进入年份识别阶段
selecting_roi_state = 0
# 建立色标 → 年份的插值函数
# 参数:
# roi: 图片中色标的区域 (numpy 数组,包含色标的像素数据)
# year_min: 色标代表的最小年份 (例如: 2014)
# year_max: 色标代表的最大年份 (例如: 2020)
# debug_name: 用于调试输出的色标名称
# 返回值:
# center_col: 色标中心列的 RGB 颜色序列 (N x 3 numpy 数组)
# interp_func: 从像素在色标中的垂直位置 (索引) 到年份的插值函数
def build_color_axis(roi, year_min=2014, year_max=2020, debug_name="色标"):
h = roi.shape[0] # 色标区域的高度
# 从 ROI 中选取中心列的像素颜色。我们假设色标是垂直的。
center_col = roi[:, roi.shape[1] // 2, :]
# 确保年份从上到下(从 year_max 到 year_min)对应像素索引 (0 到 h-1)
# 这样色条顶部 (索引 0) 对应 year_max (2020),底部 (索引 h-1) 对应 year_min (2014)
years = np.linspace(year_max, year_min, h)
print(f"\n--- 调试信息: {debug_name} ---")
print(f"ROI 高度: {h} 像素")
print(f"色标顶部颜色 (索引 0): {center_col[0]}, 预期年份: {years[0]:.2f}")
print(f"色标底部颜色 (索引 {h-1}): {center_col[h-1]}, 预期年份: {years[h-1]:.2f}")
print(f"插值映射: 索引 0 -> {year_max}, 索引 {h-1} -> {year_min}")
print(f"示例年份 (顶部, 中间, 底部): {years[0]:.2f}, {years[h//2]:.2f}, {years[h-1]:.2f}")
return center_col, interp1d(np.arange(h), years, bounds_error=False, fill_value="extrapolate")
# 匹配单个颜色到最近的色标颜色,并返回对应年份
# 参数:
# sample_color: 要匹配的单个像素颜色 (1x3 numpy 数组,RGB 值)
# color_axis: 预先建立的色标颜色序列 (N x 3 numpy 数组)
# interp_func: 对应色标的插值函数
# 返回值:
# 年份 (浮点数)
def match_color_to_year(sample_color, color_axis, interp_func):
# 计算样本颜色与色标颜色序列中所有颜色的欧几里得距离
dists = np.linalg.norm(color_axis - sample_color, axis=1)
idx = np.argmin(dists) # 找到距离最近的颜色在色标颜色序列中的索引
# 使用插值函数将找到的索引转换为对应的年份
return float(interp_func(idx))
# 鼠标点击事件处理函数 (年份识别阶段)
# 当用户点击图片时,此函数会被调用
def click_event(event, x, y, flags, param):
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN: # 检查是否为鼠标左键点击事件
global img_rgb, random_colors, random_interp, ml_colors, ml_interp
# 确保必要的全局变量已经被初始化
if img_rgb is None or random_colors is None or ml_colors is None:
print("错误:图片或色标数据未载入。请确保已成功框选色标。")
return
print(f"\n点击位置: ({x}, {y})")
# 获取点击位置的像素颜色 (RGB 值)
clicked_color = img_rgb[y, x, :]
print(f"点击像素颜色 (RGB): {clicked_color}")
# 计算点击颜色与两个色标的最小距离
random_dists = np.linalg.norm(random_colors - clicked_color, axis=1)
ml_dists = np.linalg.norm(ml_colors - clicked_color, axis=1)
random_dist = np.min(random_dists)
ml_dist = np.min(ml_dists)
print(f"与 '随机分案' 色标的最小距离: {random_dist:.2f}")
print(f"与 '机器学习' 色标的最小距离: {ml_dist:.2f}")
# 根据哪个色标的距离更小,决定点击的颜色属于哪种改革类型
if random_dist < ml_dist:
reform_type = "随机分案"
# 使用 '随机分案' 的插值函数来获取年份
reform_time = match_color_to_year(clicked_color, random_colors, random_interp)
else:
reform_type = "机器学习"
# 使用 '机器学习' 的插值函数来获取年份
reform_time = match_color_to_year(clicked_color, ml_colors, ml_interp)
print(f"结果: {reform_type}, 年份: {reform_time:.2f}")
# 鼠标事件处理函数 (ROI 选择阶段)
# 此函数只负责记录点击点和绘制临时框,状态转换由主循环控制
def select_roi_event(event, x, y, flags, param):
global roi_points, selecting_roi_state, img_raw, img_with_rois
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
roi_points.append((x, y))
# 状态转换逻辑在 main 函数中根据 roi_points 的长度进行
elif event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE:
# 在选择第一个 ROI 的第二个点时绘制临时框 (绿色)
if selecting_roi_state == 0 and len(roi_points) == 1:
temp_img = img_raw.copy() # 从原始图片复制,避免覆盖永久框
cv2.rectangle(temp_img, roi_points[0], (x, y), (0, 255, 0), 1) # 绿色临时框
cv2.imshow('点击获取年份 (请框选色标)', temp_img)
# 在选择第二个 ROI 的第二个点时绘制临时框 (绿色)
elif selecting_roi_state == 2 and len(roi_points) == 3:
temp_img = img_with_rois.copy() # 从已绘制第一个 ROI 的图片复制
cv2.rectangle(temp_img, roi_points[2], (x, y), (0, 255, 0), 1) # 绿色临时框
cv2.imshow('点击获取年份 (请框选色标)', temp_img)
# 主函数
def main():
global img_rgb, random_colors, random_interp, ml_colors, ml_interp, img_raw, img_with_rois, selecting_roi_state, roi_points
# 图片路径
img_path = 'D:/PyTorch_practice/map/x.png'
img_raw = cv2.imread(img_path) # 载入图片 (以 BGR 格式)
if img_raw is None:
print(f"错误:图片载入失败,请检查路径: {img_path}")
return
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_raw, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将图片转换为 RGB 格式
img_with_rois = img_raw.copy() # 创建一个副本用于显示和绘制永久 ROI 框
cv2.namedWindow('点击获取年份 (请框选色标)')
# 初始阶段设置鼠标回调函数为 ROI 选择模式
cv2.setMouseCallback('点击获取年份 (请框选色标)', select_roi_event)
print("--- 交互式色标框选 ---")
print("步骤 1/2: 请框选 '随机分案' 色标 (左侧蓝色条)。")
print(" 点击色标的左上角,然后拖拽鼠标到右下角并释放。")
# ROI 选择循环
while selecting_roi_state < 4: # 当 selecting_roi_state 达到 4 时表示两个 ROI 都已选定
cv2.imshow('点击获取年份 (请框选色标)', img_with_rois) # 持续显示带有永久 ROI 框的图片
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if key == ord('q'): # 按 'q' 键退出
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return
# 根据 roi_points 的长度来管理状态转换
if selecting_roi_state == 0 and len(roi_points) == 1: # 随机色标起点已点击
selecting_roi_state = 1 # 进入等待随机色标终点的状态
print("请框选 '随机分案' 色标的终点 (右下角)。")
elif selecting_roi_state == 1 and len(roi_points) == 2: # 随机色标终点已点击
# 绘制 '随机分案' 色标的永久矩形框 (蓝色)
cv2.rectangle(img_with_rois, roi_points[0], roi_points[1], (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('点击获取年份 (请框选色标)', img_with_rois) # 更新显示
selecting_roi_state = 2 # 进入准备选择 '机器学习' 色标起点的状态
print("\n步骤 2/2: 请框选 '机器学习' 色标 (右侧红色条)。")
print(" 点击色标的左上角,然后拖拽鼠标到右下角并释放。")
elif selecting_roi_state == 2 and len(roi_points) == 3: # 机器学习色标起点已点击
selecting_roi_state = 3 # 进入等待机器学习色标终点的状态
print("请框选 '机器学习' 色标的终点 (右下角)。")
elif selecting_roi_state == 3 and len(roi_points) == 4: # 机器学习色标终点已点击
# 绘制 '机器学习' 色标的永久矩形框 (红色)
cv2.rectangle(img_with_rois, roi_points[2], roi_points[3], (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow('点击获取年份 (请框选色标)', img_with_rois) # 更新显示
selecting_roi_state = 4 # 两个 ROI 都已选定,退出循环
# 色标选择完成后,提取坐标并建立颜色轴
# 确保坐标是正确的 (x_start, y_start, x_end, y_end) 格式,并且 start <= end
random_roi_coords = (min(roi_points[0][0], roi_points[1][0]), min(roi_points[0][1], roi_points[1][1]),
max(roi_points[0][0], roi_points[1][0]), max(roi_points[0][1], roi_points[1][1]))
ml_roi_coords = (min(roi_points[2][0], roi_points[3][0]), min(roi_points[2][1], roi_points[3][1]),
max(roi_points[2][0], roi_points[3][0]), max(roi_points[2][1], roi_points[3][1]))
# 从原始 RGB 图片中提取 ROI 图片数据
random_roi = img_rgb[random_roi_coords[1]:random_roi_coords[3], random_roi_coords[0]:random_roi_coords[2]]
ml_roi = img_rgb[ml_roi_coords[1]:ml_roi_coords[3], ml_roi_coords[0]:ml_roi_coords[2]]
# 建立两个色标的颜色轴和插值函数
random_colors, random_interp = build_color_axis(random_roi, debug_name="随机分案色标")
ml_colors, ml_interp = build_color_axis(ml_roi, debug_name="机器学习色标")
# 转换到年份识别阶段
cv2.setMouseCallback('点击获取年份 (请框选色标)', click_event) # 将鼠标回调函数改为年份识别模式
cv2.setWindowTitle('点击获取年份 (请框选色标)', '点击获取年份') # 更新窗口标题
print("\n色标框选完成。现在请点击地图上的省份以获取年份。按 'q' 键退出。")
# 年份识别循环
while True:
cv2.imshow('点击获取年份', img_with_rois) # 继续显示带有永久 ROI 框的图片
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
|